
03 Oct, 2024 Relief: Proven Methods to Heal and Get Back in the Game
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis) is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation on the inner side of the elbow, where the tendons of the forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of the elbow. The pain may spread into the forearm and wrist. Golfer’s Elbow is similar to Tennis Elbow, which occurs on the outside of the elbow. The condition is commonly caused by repetitive stress or overuse of the muscles and tendons of the forearm, particularly in activities like golfing, racket sports, throwing sports, weightlifting, and occupations that require repetitive wrist and finger motions.
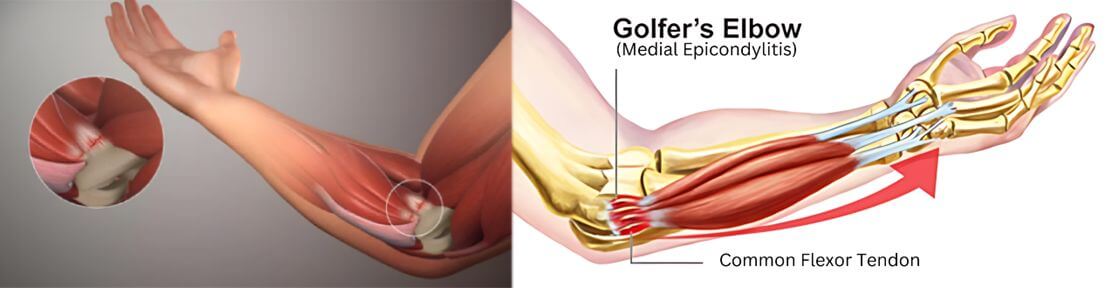
Symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow:
- Pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow.
- Stiffness in the elbow.
- Weakness in the hands and wrists.
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers, especially the ring and little fingers.
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers, especially the ring and little fingers.
Common Causes of Golfer’s Elbow:
- Repetitive Motions: Activities that involve repetitive wrist flexion, gripping, or twisting can strain the forearm muscles and tendons. This is common in sports like golf, baseball (particularly pitching), tennis, and weightlifting.
- Improper Technique in Sports: Using improper techniques or equipment (e.g., too heavy a golf club or tennis racket) can put excessive strain on the tendons and muscles of the forearm, leading to injury.
- Overuse Injuries: Engaging in activities that require repetitive motions over an extended period without adequate rest can lead to Golfer’s Elbow. This can occur in both sports and occupational settings.
- Forceful and Repetitive Gripping: Occupations or hobbies that involve heavy lifting, hammering, painting, carpentry, plumbing, or any activity requiring strong, repetitive wrist movements can increase the risk.
- Poor Conditioning or Weak Muscles: Lack of proper conditioning, weak forearm muscles, or limited flexibility can increase stress on the tendons, making them more prone to injuries.
- Inadequate Warm-Up or Stretching: Failing to properly warm up or stretch the muscles and tendons before engaging in activities can increase the risk of strain and injury.
- Sudden Increase in Activity Level: Increasing the duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity too quickly without proper training or preparation can result in Golfer’s Elbow.
- Direct Trauma to the Elbow: A direct blow or impact to the inside of the elbow can sometimes cause damage to the tendons, leading to inflammation and pain.
Effective Treatments to Relieve Pain
1. Rest
The first step in treating Golfer’s Elbow is giving your arm enough time to rest. Avoid any activities that cause pain or strain on the elbow. Resting allows the inflammation to subside and prevents further damage to the tendons.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain. Ice therapy is a simple yet effective way to manage the symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow, especially in the early stages.
3. Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These medications should be taken as directed and can provide relief during flare-ups or when performing daily activities.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a crucial component in the recovery process. A physiotherapist will guide you through stretching and strengthening exercises designed to restore flexibility and strength to the forearm muscles. Consistent physical therapy can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent future occurrences.
5. Brace or Strap
Wearing a counterforce brace or strap can help alleviate stress on the tendons, reducing pain during activities that involve gripping or lifting. The brace works by redistributing the pressure away from the damaged area, offering support and relief.
6. Corticosteroid Injections
For severe cases where pain persists despite other treatments, corticosteroid injections may be recommended. These injections help reduce inflammation and provide quick, albeit temporary, relief from pain. However, they are typically used as a last resort due to potential side effects.
7. Surgery
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief after several months, surgical option might be considered after discussing it with an Orthopedic surgeon. The surgical procedure involves removing the damaged tendon tissue to promote healing. This option is generally reserved for chronic cases where the condition severely affects quality of life and function.
Conclusion
Golfer’s Elbow can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, but with the right treatment approach, managing pain and regaining full function is achievable. From simple remedies like rest and ice therapy to more advanced options such as physical therapy and surgery, there are numerous effective treatments available. If you’re experiencing symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow, it’s essential to consult with an Orthopaedic specialist. The experts at A+ Orthopaedic and Sports Med Center are here to provide a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs, helping you get back to your best, pain-free.
