Wrist Arthroscopy
Indications
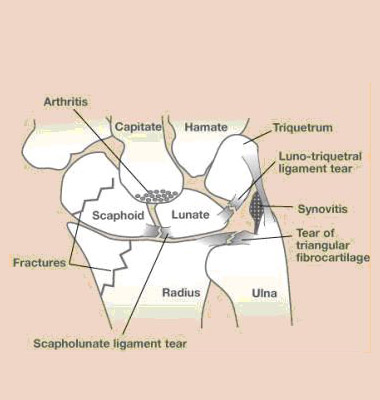
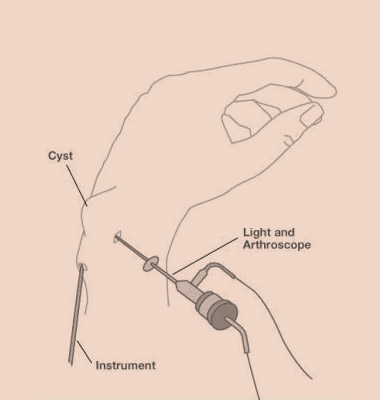
Wrist arthroscopy allows the visualization of the cartilage surfaces of all bones in the wrist and better evaluation of the ligaments between the various bones of the wrist. Frequently after an injury, pain, clicks, and swelling may be indicative of an internal problem in the wrist. Arthroscopy is often the best way of assessing the integrity of the ligaments, cartilage, and bone. When wrist problems are encountered, many are treated through these small incisions using specialized equipment available for wrist arthroscopy. Often arthroscopy is used to aid in the reduction of fractures of the bones of the wrist. Wrist arthroscopy is also used to assess the integrity of the TFCC (triangular fibrocartilage, or meniscus of the wrist). Today, wrist arthroscopy can even be used to remove some ganglions of the wrist and to assess the extent and treatment of various types of arthritis of the wrist.
Procedure
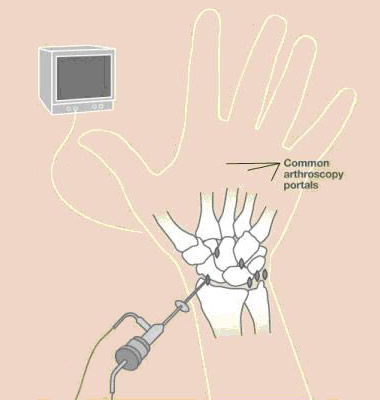
A small camera fixed to the end of a narrow fiber-optic tube (2.7mm wide) is inserted through a small incision in the skin (about 5mm long) directly into the back of the wrist joint. The camera lens magnifies and projects the small structures in the wrist onto a television monitor, allowing for more accurate diagnosis. Several small incisions (portals) are used to allow the surgeon to place the camera in different positions to see different structures inside the joint as well as to place various small instruments into the wrist joint to help diagnose and treat various problems in the wrist. The wrist is usually distracted and fluid is infused into the joint to expand the joint and allow improved visualization during the procedure. Sometimes wrist arthroscopy is combined with open procedures.