- Mon - Sat
08:00am - 08:00pm

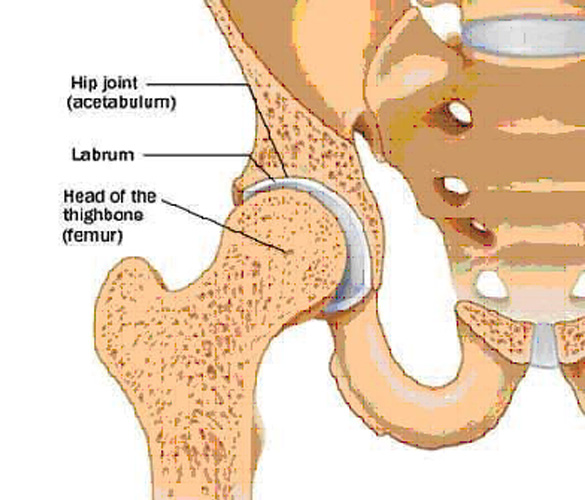
The socket of your hip joint (acetabulum) is lined by cartilage called labrum. This cartilage provides stability and cushioning for your hip joint, allowing the ball of your thighbone (femur) to move smoothly and painlessly in the socket.
A tear in your labrum, known as a hip labral tear or acetabular labral tear, can result from injury, repetitive movements that cause wear-and-tear on your hip joint,
In many cases, a hip labral tear causes no signs or symptoms and doesn’t require treatment. Occasionally, however, a hip labral tear may cause pain or a “catching” sensation in the hip joint.
Treatment for a hip labral tear consist of physical therapy, medications or a combination. Sometimes an arthroscopy surgery is necessary to treat a hip labral tear.
Many hip labral tears cause no signs or symptoms. Occasionally, however, you may experience one or more of the following:
The following factors may increase your risk of a hip labral tear:
The doctor A+ clinic will ask about your symptoms and conduct a physical examination.
To confirm the diagnosis of a hip labral tear, you may undergo an MRI
Many hip labral tears cause no signs or symptoms and need no treatment. However, when treatment is necessary it may include:
Once the surgeon can see the joint, the specialized instruments needed to perform the procedure are inserted through small accessory incisions. Depending on the cause and extent of the tear, the surgeon may cut out and remove the torn piece of labrum or repair the torn cartilage with a suture procedure.
A program of lower extremity strength training and core stability exercises may help you prevent lower extremity injuries in general, including hip labral tear.