- Mon - Sat
08:00am - 08:00pm

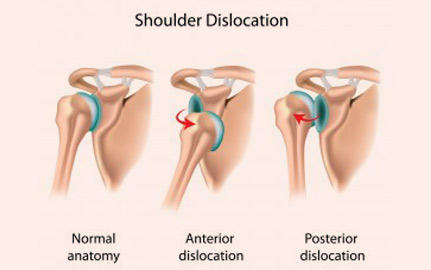
Shoulder dislocation is a common shoulder injury in contact sports such as cricket, football, basketball and martial arts.In our country it is also frequently seen after road traffic accident (RTA). A dislocated shoulder is characterized by severe shoulder pain which requires immediate treatment to restore normal shoulder anatomy.
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that has a large degree of range of motion. It has been compared to a golf ball on a tee. Though this makes the joint more mobile but inherently less stable.
The shoulder joint is enclosed by a fibrous capsule which is strengthened by ligaments that provide a reinforced thickening of the capsule. The joint also has a labrum – a fibro cartilage lip that increases the stability of the joint. In case of a dislocation due to trauma (such as a fall or collision), the capsulolabralcomplex gets detached from the anterior glenoid.This detachment of the capsulolabral complex is called a Bankart lesion. A bankart lesion is usually accompanied by Hillsach’s lesion of the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head. Studies have shown an increase in rate of dislocation in patients of age less than 20 years who have dislocated there shoulder and are likely to present with recurrent dislocations. The term recurrent dislocation means that a person has had two or more episodes of dislocations of the shoulder. Recurrent dislocation can be very debilitating condition with each episode causing more damage to the joint.
The arm is normally held in the shoulder socket by the soft tissue capsule which fits over the joint like a socket. It is also held together and stabilized by fibrous ligaments that lie within the capsule, by the muscles and tendons that rotate the arm.
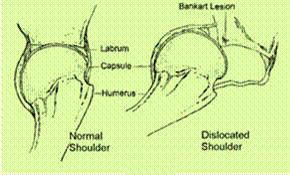
Instability is usually defined as a clinical syndrome which occurs when a shoulder is loose enough to produce symptoms. It can refer to either outright dislocation where the upper arm bone comes out of the socket or to a more subtle slipping of the humeral head within the socket, a condition known as subluxation.
Shoulders can dislocate when a strong force, such as a traumatic injury, abnormally stretches the ligaments and capsule, causing the ball-shaped end of the humerus to pop out of its socket. A minority of people have shoulders that can subluxate or even dislocate spontaneously. However, almost 95% of shoulder dislocations result from either a forceful collision or from a sudden wrenching movement as may occur during sport, from falling onto an outstretched arm, and from motor vehicle collision.
During the period when your shoulder is dislocated, bruising, swelling, weakness, tingling,numbness and/or loss of sensation typically occur.
The most obvious symptom is shoulder pain. A person with a dislocated shoulder will be unable to move the affected shoulder and will hold the arm protectively against the chest. The normal rounded appearance of the shoulder will be replaced by a more squared-off edge because the head of the Humerus lies outside the joint.
If a dislocation is suspected, an x-ray should be taken to confirm the damage.
Apply ice packs/cold therapy to relieve pain and swelling.
Wear an Arm sling for support.
It is important that a shoulder dislocation is seen quickly by a doctor who can put the joint back in place. A dislocated shoulder joint can cause damage to the Axillary nerveand a larger Hillsach’s lesion of the humeral head. Damage to this nerve leads to a loss of sensation and decreased muscle strength in the affected arm. NSAIDs(Antiinflammatory) medication prescribed by a doctor can help to relieve the shoulder pain and swelling.
Ice packs can be applied to the injured shoulder for 20 minutes every two hours (never apply ice directly to the skin). The ice packs relieve pain and reduce swelling in the damaged tissue.
Once the shoulder has been put back in place it is immobilized using a sling. The sling is kept on till you are pain free. During this period it is important that the elbow, wrist and fingers are mobilized to prevent stiffness of these joints.
Active rehabilitation is started as soon as possible but overhead arm movement and any sporting activity should be avoided for at least 6 weeks. Gentle range of movement exercises under the supervision of a physiotherapist can be started once the sling is removed. Strengthening exercises for the Rotator Cuff muscles should be started as soon as they can be done without pain.
Because of the damage to the structures surrounding the shoulder(Soft tissue Bankart or Bony Bankart), there is a high chance of recurrent dislocation. Surgery on an unstable shoulder is usually required after two dislocations or more.
Once there has been a dislocation of the shoulder, the joint will have a degree of instability and is more likely to dislocate again. This is because the ligaments, capsule labrum and humeral head are damaged. This makes the joint unstable and cannot restrain the head within the joint cavity. In order to prevent dislocation, the Rotator Cuff muscles that surround the humeral head should be strengthened.
The Rotator Cuff muscles (Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor and Subscapularis) are a group of four muscles situated around the shoulder joint. Although they have individual actions, their main role is to work together to stabilize the humeral head (ball) in the shoulder socket. Exercises using a resistance band can be very effective at strengthening the Rotator Cuff and maintaining shoulder stability and prevent recurrent shoulder dislocation.
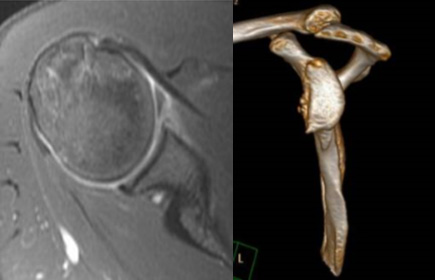
You would have to undergo a thorough checkup with a shoulder surgeon who will recommend an X-ray, and MRI with or without a 3D CT scan of the shoulder.